Language, Cognition and Scaffolding
2. Cognitive engagement
2.2. Teaching to think
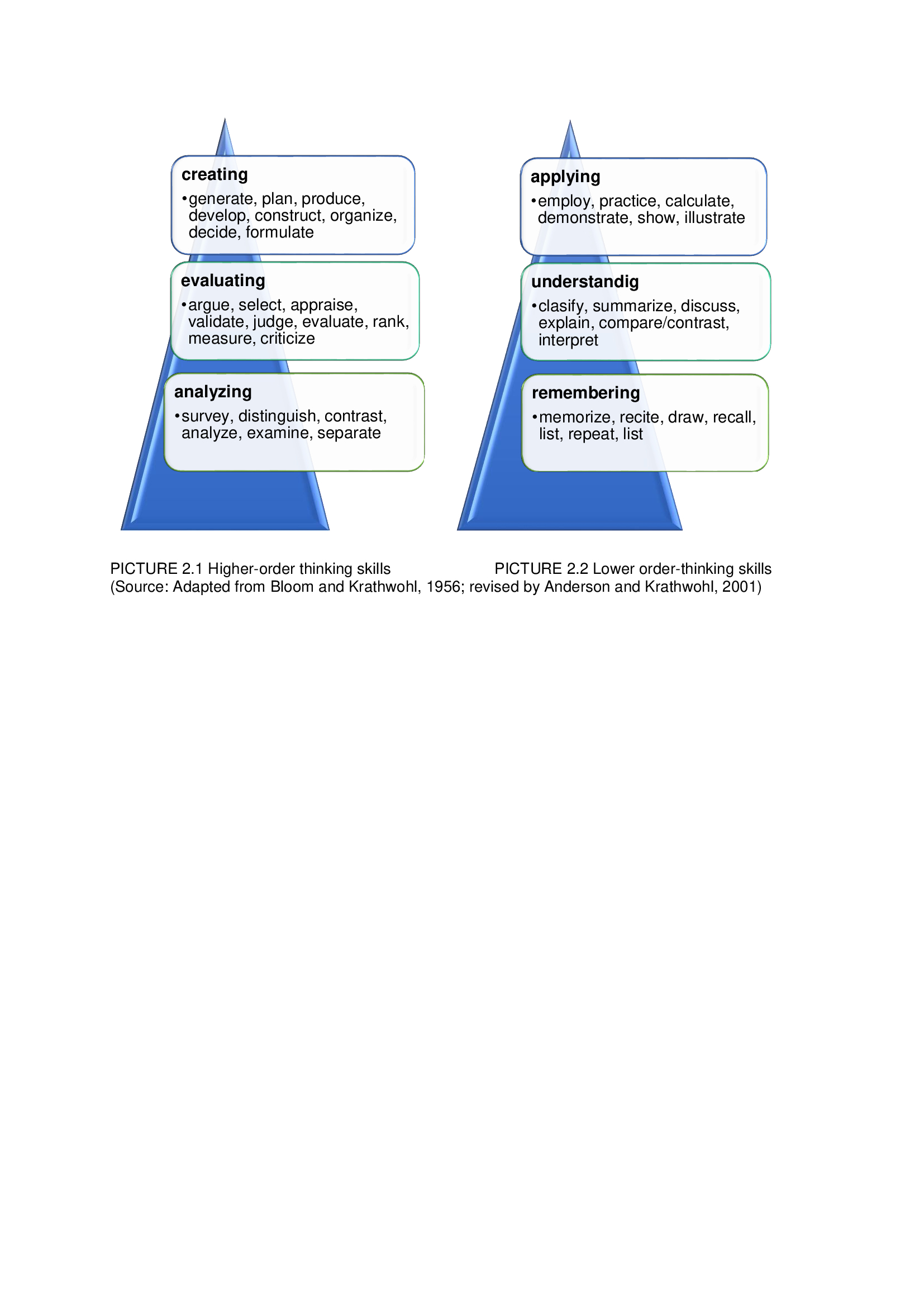
Bloom’s taxonomy was created in 1956 to classify the thinking levels. A taxonomy is a system of classification which provides a conceptual framework. Bloom’s Taxonomy is simple, easy to remember and easy to apply. Cognitive processes were divided by Bloom into lower-order thinking - LOT (remembering, understanding, applying) and higher-order thinking - HOT (analysing, evaluating, creating), both of which are integral to effective learning.
According to Fredericks (2005), approximately 80 per cent of all the questions teachers tend to ask are factual, literal, or knowledge-based. The result is a classroom in which there is little creative thinking taking place. Therefore, Meyer (2010) recommends focusing on higher-order thinking skills. It means applying higher-order thinking processes in the tasks performed by students. As he emphasises, it is the key to success in the Information Age. It is not easy for the teachers as it requires comprehensive planning of tasks, vocabulary and scaffolding.