Language, Cognition and Scaffolding
3. Scaffolding
3.2. Tasks promoting language development
Word level
The teacher knows that the class will be unable to describe the photograph immediately without understanding the context. The hope is to engage students, that they may develop both thinking skills and vocabulary. The photograph will also supply the focus for a writing task. Here are the questions:
How many people are there?
Who are these people?
Where are they?
How do you know this?
When was the photograph taken (winter, summer, daytime, weekend)?
What are these people doing?
How do they feel?
From word level to sentence level
The first
three questions are straightforward that might be answered using a single word
(a number, a name or yes/no). The following question raises the thinking level
and invites reasoning and speculation rather than mere observation. The fifth
one: The teacher can give vocabulary headers (in the target language) to
respond to question five, such as weather: cloudy, sunny, temperature; light:
dawn, midday, evening. The teacher can provide sentence beginnings to respond
to question six. They are sitting…, They are playing…, They are jumping.
Text level
Learners
can be given a written task similar to Describe the picture to a friend who
hasn't seen it. The teacher can add one more scaffolding tool: a
substitution table.
|
I think that |
they are |
happy |
because they are |
jumping |
|
|
running |
|
||||
|
cold |
laughing |
|
|||
|
playing |
|||||
|
some of the children are |
hot |
||||
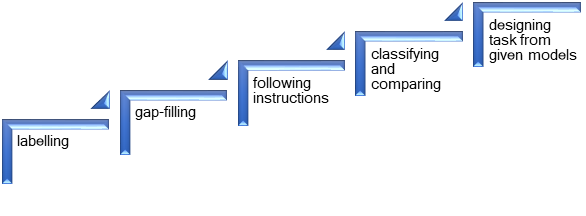
Figure Chain of task types
The sequence begins at word level with the introduction of new concepts and their related vocabulary and definitions. The second and third steps work the reinforcement of vocabulary and concepts. The fourth step is based on a hands-on activity, creating a clay model representing a landscape, which has to be described with the help of a substitution table. At this level, students are requested to describe and compare the landforms.